Weekly Task - Topic 5
Can effectuation also be used in companies? Or is it useful only for entrepreneurship?
Chong - In short, effectuation can be used to businesses and entrepreneurship, to put it in lengthy answer form, we must first define effectuation in order to determine if it can be used to businesses. Effectuation is how someone thinks and makes choices based on the idea that entrepreneurs create their future by taking action and making things happen. It is a mindset that helps create opportunities and problem solve with the limited resources available to help them, rather than taking a gamble to plan for the future (Dew, n.d.).
After learning the meaning of effectuation, we can truly make sure that it can be used for companies as well. Since business growth is associated with entrepreneurship, research is one of the central topics. Entrepreneurship has intensified, and a and a brand new theoretical view of vision has arisen from it to explain the behavior of entrepreneurs (Matalamäki et al., 2017). One of the most emerging theories in entrepreneurship is effectuation. Effectuation has a deep connection to the early stages of the development of an organization and was just recently introduced as a logic potentially applicable to existing businesses (Jiang & Rüling, 2017). It suggests that existing businesses can benefit from implementation principles in decision-making processes.
Hence, like I said before, yes, effectuation can be used for company as well as for entrepreneurship. {225 words}
What is the key difference between effectuation and other approaches in entrepreneurship?
Nareen - The key difference between effectual approach and other approaches in entrepreneurship is how the entrepreneur starts off with their business. One of the other approaches include causal approach or reasoning in entrepreneurship which is the opposite of effectual.
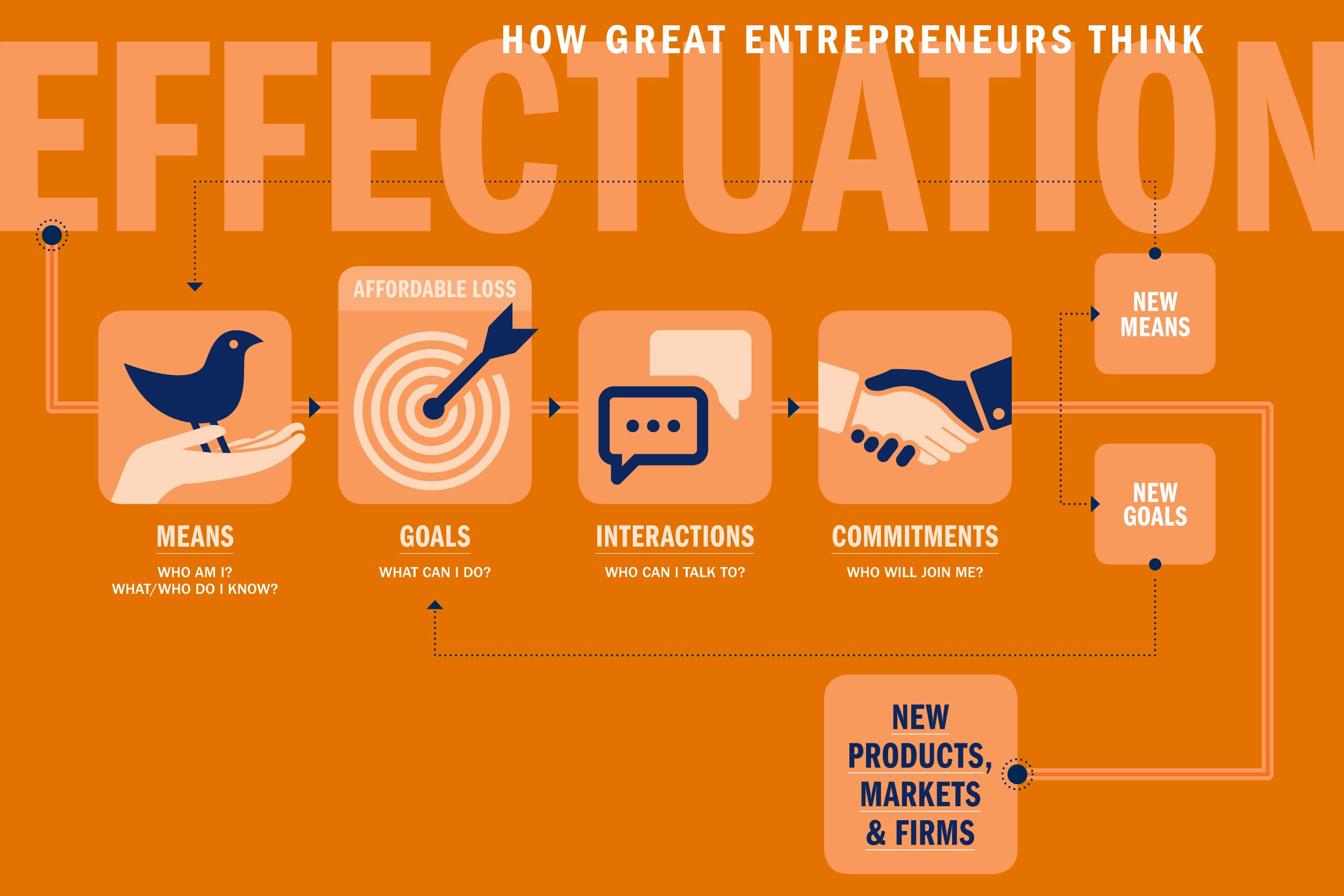
Effectual approach is means-oriented and starts with the means available, with goals emerging and evolving over time. In this approach, the entrepreneur begins with the available means and identify goals that can be achieved with those means. Effectual reasoning unlike causal, operates assuming the future can change anytime. Characteristics of effectual reasoning include imagined and evolving goals. Effectual reasoning involves a process of trial and error, where the entrepreneur experiments with different means and allows the goals to emerge and evolve over time (Dew, n.d.).
On the other hand, causal approach also known as goal-oriented reasoning, is a standard approach to entrepreneurship. In this approach, the entrepreneur starts off with a clear and specific predefined goal without any means. Causal reasoning operates on the assumption that the future is predictable and controllable. Characteristics of causal reasoning include clearly specified and given goals. Entrepreneurs have to rely on market research and analysis to identify opportunities and threats for the future (Sarasvathy, 2001). {203 words}
Are the effectual approach and traditional (causal) approach mutually exclusive?
Luven - The effectual approach and causal approach are two different mindsets that can be implemented in a company's entrepreneurship venture. The causal approach, derived from the word "causation", focuses on selecting the ways for the given effect, like a many-to-one mapping. On the other hand, the effectual approach would accept the way given and then select from the possible effects that can be made, like a one-to-many mapping (Sarasvathy, 2001).
Although different, they are not to be considered mutually exclusive as the effectual approach was not made to replace the causal approach, while it was made as another way to achieve business goals. The reason they are not mutually exclusive is because both approaches might share certain traits during decision-making, therefore it is situational and may co-exist (Morales, 2020). As factual proof, Sarasvathy (2001) mentions these two decision logics are not mutually exclusive, and has observed there would be combinations of both approaches during the entrepreneurial process. Moreover, the simultaneous usage of the two decision logics causes a synergy that improves opportunity, business model innovation and venture performance.
Distinguishing the different approaches for a business would be based on
the current information the company has, looking into those patterns
and then identifying what would be the effective approach for the
existing information (Morales, 2020). {214 words}
Does effectuation mean: "not planning"?
Naviin - No, effectuation does not mean "not planning", instead it involves and consists of little planning. According to Dargham (2021), effectuation primarily means the way of thinking of entrepreneurs by putting consistent effort into achieving something meaningful in the unpredictable future. Rather than planning the future predictively, effectuation takes the current available resources and utilizing it while building goals along the way. Although effectuation does not directly mention planning, it still contains some different approach of planning, rather than the traditional planning methods used with specific goals.
To support the term effectuation, there are several principles revolving around it. First, the basic one would be the Bird-In Hand principle, which involves entrepreneurs starting with basic available resources in creating solutions and taking action. Next, according to Sarasvathy's principles, the Lemonade Principle contains the mindset of embracing mistakes and surprises as it is inevitable and turn it into future solutions and strategies. Besides that, taking calculated risks and being able to afford the losses are one of the key concepts of Affordable Loss principle.(Sarasvathy, 2001). Moving on to the Crazy Quilt principle, which involves the process of meeting new people and forming partnerships to create valuable funds and obtaining resources. Lastly, Pilot in the Plane principle refers to the mindset of entrepreneurs who should believe they are the one capable of shaping their own future. {222 words}
Are effectuation and lean startup compatible?
Sze Jay - Effectuation and Lean Startup are two distinct approaches to entrepreneurship, each offering unique perspectives on the process of creating and managing a new venture. Effectuation, developed by Saras Sarasvathy, emphasizes leveraging existing resources and focusing on controllable factors to create opportunities. It prioritizes the entrepreneur's abilities to adapt and shape the future rather than predict it (Sarasvathy, 2001).
On the other hand, Lean Startup, popularized by Eric Ries, advocates for a systematic approach to developing businesses and products through validated learning. It emphasizes iterative experimentation, customer feedback, and rapid prototyping to minimize waste and increase the likelihood of success (Ries, 2011).
While they may appear divergent, there are areas of compatibility between effectuation and Lean Startup. Both emphasize the importance of action and learning from experience. Effectuation's focus on leveraging existing resources aligns with Lean Startup's emphasis on rapid experimentation and customer feedback to iteratively refine the business model (Shivdas, 2022).
Moreover, the principles of effectuation can inform the Lean Startup process by helping entrepreneurs identify and utilize available resources more effectively, thus enhancing the efficiency of experimentation and iteration. In this way, while effectuation and Lean Startup may have different theoretical underpinnings, they can complement each other in practice, offering entrepreneurs a more comprehensive toolkit for navigating the uncertainties of entrepreneurship. {210 words}
Sarasvathy, S. D. (2001, April 1). Causation and effectuation: toward a theoretical shift from economic inevitability to entrepreneurial contingency. Academy of Manageent Review. 26 243–263. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.2001.4378020
Dew, N. (n.d.) What is Effectuation? Effectuation 101. https://effectuation.org/effectuation-101
Matalamäki, M., Vuorinen, T., Varamäki, E., & Sorama, K. (2017). Business growth in established companies; Roles of effectuation and causation. Journal of Enterprising Culture, 25(02), 123–148. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218495817500054
Jiang, Y., & Rüling, C. (2017). Opening the black box of effectuation processes: characteristics and dominant types. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 43(1), 171–202. https://doi.org/10.1177/1042258717744204
Ries, E. (2011). The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses. Crown Publishing Group. https://www.academia.edu/6418358/The_Lean_Startup_How_Today_s_Entrepreneurs_Use_Continuous_Innovation_to_Create_Radically_Successful_Businesses
Dargham, A. (2021, January 7). Effectuation principles: a theory for entrepreneurs | DAA Capital Partners. https://www.daacap.com/effectuation-principles-a-theory-for-entrepreneurs/
Shivdas, A. (2022) Is there a difference between Effectuation and Lean StartUp Methods? ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/post/Is_there_a_difference_between_Effectuation_and_Lean_StartUp_Methods#:~:text=The%20basic%20relationship%20between%20the,quickly%20and%20inexpensively%20as%20possible.

Comments
Post a Comment